Table of Contents
Beware, what you see and hear online may not be the truth. Thanks to deepfake technology, anyone can create a convincing video or audio of someone saying or doing something they never actually did. The rise of deepfakes poses a significant threat to our society, from political propaganda to celebrity defamation. In this blog, we’ll answer the question: “What are deepfakes?”
Deepfakes can negatively impact brands and creators, but the good news is that scientists and researchers are working tirelessly to develop deepfake detection tools that can help us identify falsified media. Keep reading to learn about the potential dangers and the latest advances in fake media detection.
So What Are Deepfakes?
They’re the latest digital threat that’s making waves in the world of technology. Deepfakes are videos or images altered using machine learning algorithms to replace a person’s face or voice with someone else’s.
They can be used to create fake news, political propaganda, and even pornography. What’s even scarier is that with the advancement of deep learning technology, these videos are becoming more and more convincing, making it hard to tell what’s real and what’s not.

The “deep” in “deepfake” refers to the deep learning technology used to create these videos. By learning from large datasets of images and videos, algorithms can generate imitations of real people almost indistinguishable from the real thing. But fake news is not just a fun experiment in technology. They pose a serious threat to society by spreading misinformation and manipulating public opinion.
What Are Deepfakes Used For?
- Textual deepfakes: AI can create false articles, poems, blogs, and other writing pieces.
- Audio deepfakes: Most commonly used for scams, pretending that the person calling is a trustworthy figure like a CEO or CTO.
- Image and video deepfakes: Depict a person saying or doing something they did not do or appearing in a manner different from reality. For images, AI generates or manipulates fake images so they appear realistic.
- Face-swapping deepfakes: Created by transposing a deepfake face onto someone else’s face, with the deepfake face acting as a mask.
- Synthetic media: Refers to any media created or modified with the help of AI, including deepfakes.
- Speech synthesis deepfakes: Use AI to create realistic fake audio of someone’s voice.
How Are They Created?
The question, “What are deepfakes” extends past their uses. Neural networks, the backbone of deepfake technology, create deepfakes. These networks provide machine learning algorithms that manipulate visual and audio content to create convincing imitations of real people.
To generate a deepfake, creators use neural networks trained on extensive hours of actual video footage of a person. This enables the neural network to comprehensively understand the person’s appearance, including how they look from various angles and under different lighting conditions.
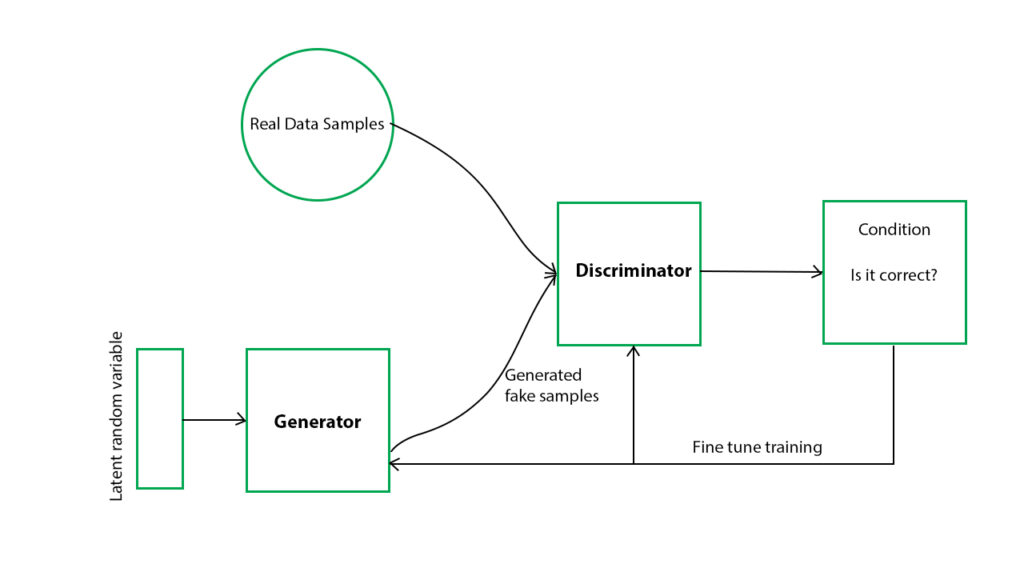
An alternative method for creating deepfakes involves using a generative adversarial network (GAN), which involves two opposing algorithms working against each other.
The first algorithm, or generator, produces a fake image or video, while the second algorithm, or discriminator, attempts to identify whether the content is authentic. This back-and-forth process continues until the generator produces images or videos that the discriminator algorithm cannot distinguish as fake.
What Are Deepfakes’ Impacts on Society?
Sadly, fake news has become a significant concern for our society due to its ability to spread disinformation and manipulate public opinion. These AI-generated videos have the potential to distort the democratic process.
In the recent South Korean presidential election, one of the candidates relied heavily on deepfakes as a campaign tool. Yoon Suk-yeol, who was running for the opposition People Power Party, had numerous hours of recorded footage of himself transformed into a deepfake video. This fake video was intended to help Yoon Suk-yeol better connect and engage with potential voters during the election campaign.
In other cases, falsified media has been used for malicious purposes, such as revenge porn or harassment. Fake media has also targeted celebrities, influencers, and public figures. These videos and images are intended to damage their reputations and spread false information about them. Overall, fake news has the potential to threaten the integrity of information and media.
What Are Deepfakes’ Impact on Creators and Brands?
The rise of deepfake technology has brought both opportunities and challenges to creators and brands. On the one hand, deepfakes can be used as a creative expression and marketing tool, such as creating realistic virtual models for fashion shows or using deepfake technology to raise awareness about social issues.
On the other hand, deepfakes can also be used for harmful purposes, such as nonconsensual pornography and political disinformation, causing reputational damage and financial fraud. Brands and creators need to be aware of the potential risks of deepfakes and take proactive measures to protect their reputations and audiences.
This may include educating their consumers about the dangers of deepfakes and implementing detection and prevention tools to mitigate the risks of deepfakes being used against them.

How Do You Spot Them?
So, now that you can adequately answer the question, “What are deepfakes,” another question remains. How do you spot them? Uncovering falsified media can be challenging. However, a handful of methods can be utilized to unveil this sophisticated AI-generated media.
Look for subtle signs of manipulation, such as inconsistencies in lighting, shadows, or reflections. Paying close attention to the face can also reveal tell-tale signs of deepfakes, such as strange facial expressions or movements. Additionally, audio deepfakes can be detected by comparing them to high-quality audio recordings or analyzing speech patterns and ambient noise.
Specialized tools and methods, such as deepfake detection challenges and software that analyzes images and videos, can also help detect deepfakes. Live deepfakes can be caught by analyzing eye blinking patterns or asking the person to turn their profile to the camera. Tracking eye blinking patterns can help you uncover deepfakes.
Concluding Thoughts
Hopefully, we answered the “what are deepfakes” question, so keep your eyes peeled for falsified media. This is especially important when researching influencers and their reputation. If a piece of information or media concerns you, be sure to do your research. Fake news can make or break the reputation of yourself, brands, or other creators, so you must stay alert!