Table of Contents
To solve issues of heavy usage, slow processing time, and high gas fees, Polygon was developed as a solution following the evolution of Bitcoin and then Ethereum. But what is Polygon and how does it work?
Problem Solving
In a past article, we talked about the issues of Ethereum. To sum it up here, the issue revolves around the fact that when Nakamoto made Bitcoin back in 2009, its functionality couldn’t account for the millions of transactions that happen on an open Blockchain. When Nakamoto started Bitcoin, there were only a few laptops that were running the network and creating Bitcoin. Processing power was limited to the CPUs of the laptops in 2009.
The next evolution in Blockchain technology came with Ethereum. Ethereum was both more efficient and utilitarian than its predecessor. Along with having a blockchain that could retain value, this cryptocurrency could store bits of code and smart contracts. This allowed Ethereum to be integrated into decentralized applications (dApps).
However, Ethereum still had the same problem as Bitcoin in that it couldn’t process transactions fast enough. Along with that, as the Ethereum network became used heavily at its limits, the gas fees (fees used to maintain the network and pay the miners) became more expensive.
This is where Polygon comes in, but what is Polygon?
Via Polygon
What is Polygon?
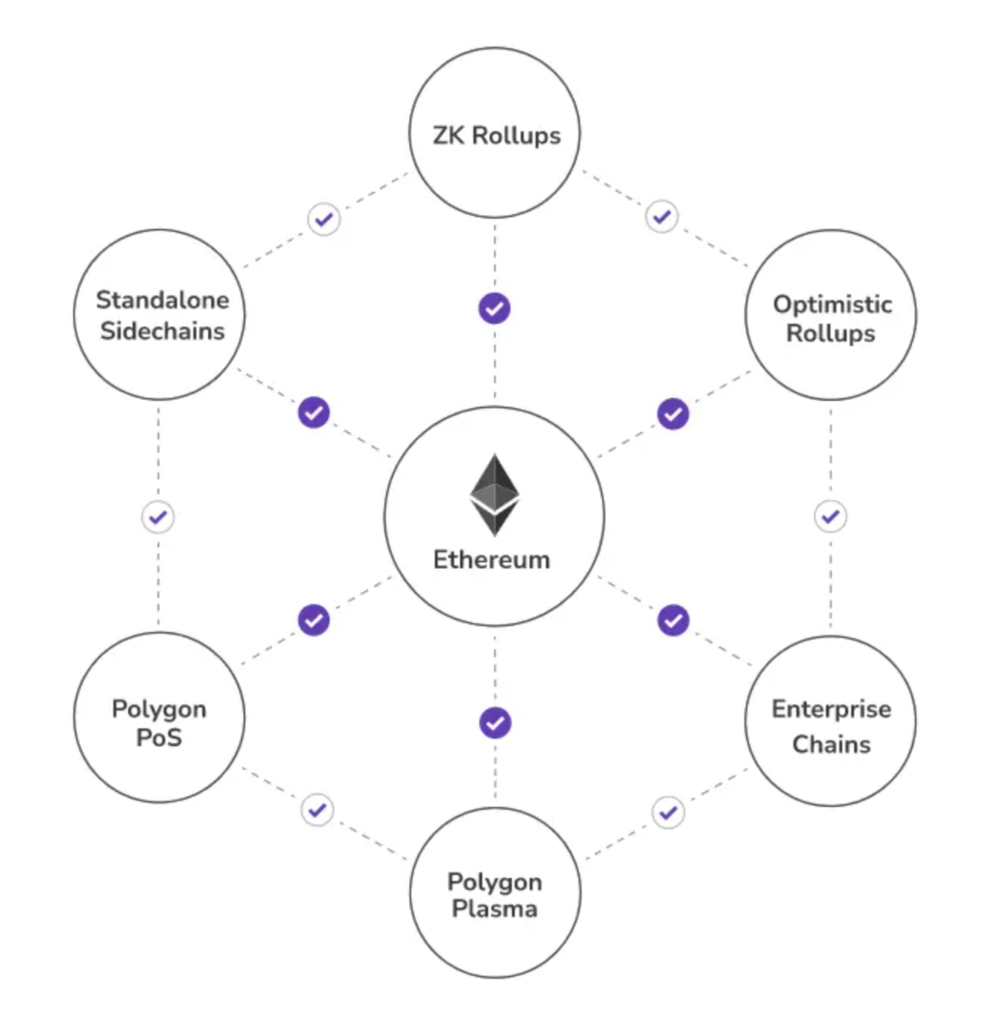
At its founding, Polygon was meant to solve Ethereum’s scalability problem. This blockchain does not seek to replace Ethereum like other 2-layer solution blockchains like Avalanche.
Instead, Polygon acts as a layer that you can add to Ethereum. It does not change the underlying blockchain but acts as a way for Ethereum to expand in size. It also brings greater security, efficiency, and usefulness.
When we look at what Polygon brings to the table. We see that it can speed up Ethereum transactions and lower the cost to under a cent. This technology can be integrated into dApps to ensure that the developers never have to worry about congestion.
They do this by handling Ethereum’s transactions on a separate blockchain and then returning the transaction back to Ethereum so that the post-processing can be handled by the Ethereum blockchain.
Via Coin Central
If you want to know about DAO, Crypto’s next big thing, read more here.
How does Polygon work?
A perfect analogy for how Polygon works comes from the Coinbase website.
In this analogy, Ethereum is a train that goes from point A to point B. Along the way, it might have 40 stops. It stops at every town and at every station in between towns. This is good for getting people from point A to point B, but it is very slow as you have to wait 10 minutes at every stop for people to come aboard and depart.
Polygon is like a train that runs parallel to this train but only stops at 2 or 3 stops in major towns or cities. People joining Polygon can go larger distances faster and then use the original train to go smaller distances.
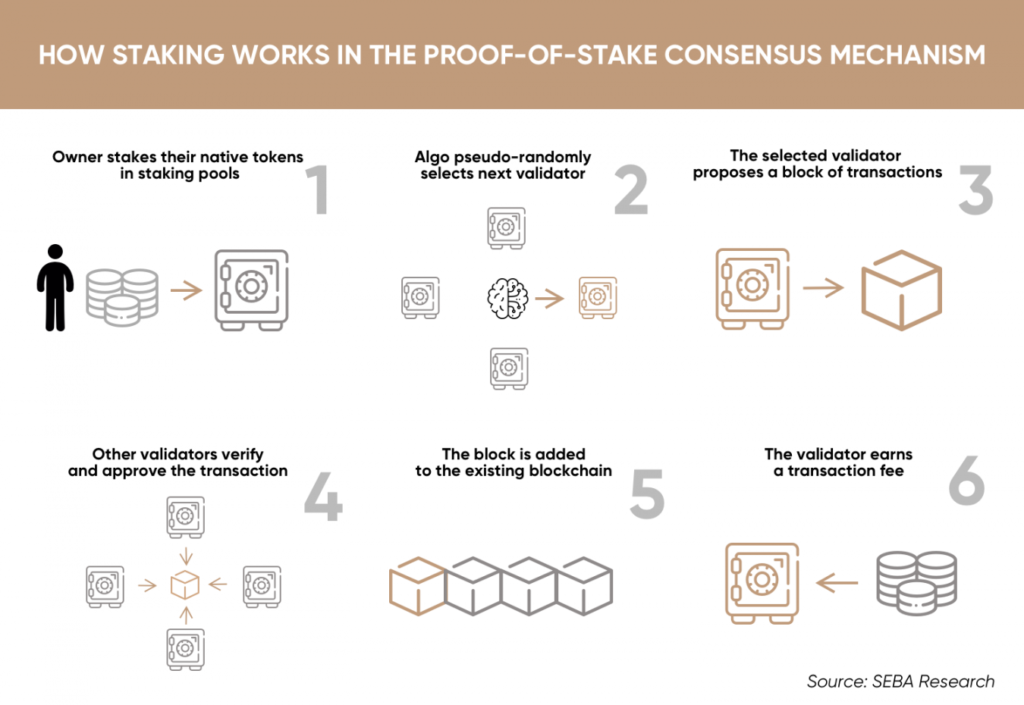
Polygon’s Consensus Mechanism
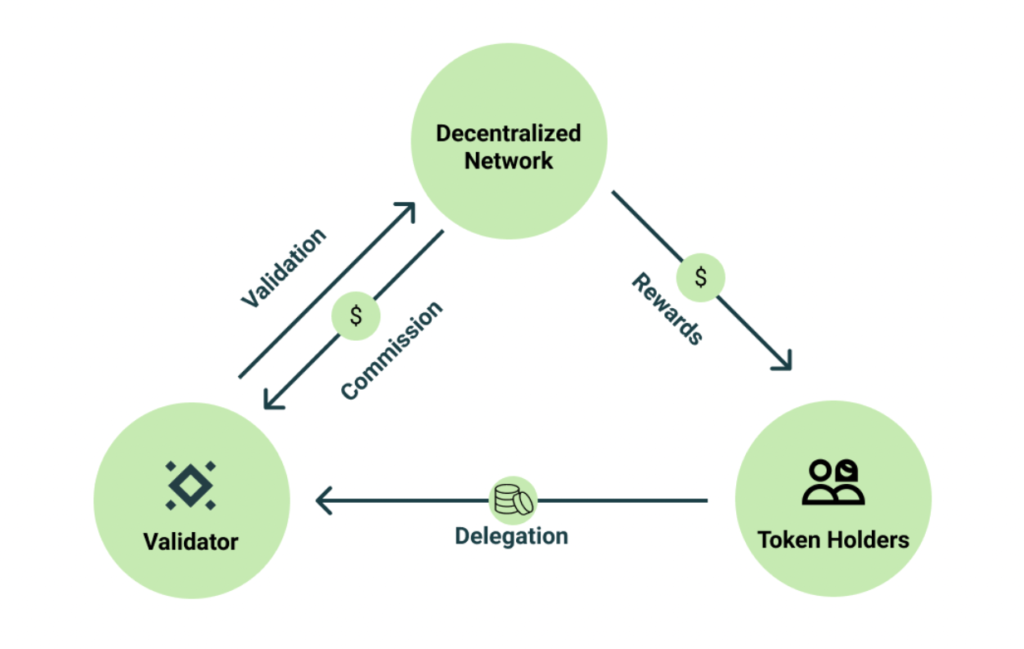
Polygon uses a Proof-of-stake consensus mechanism. To break that down, Polygon has a specific way to come to a consensus that validates that transactions are correct and receive the reward. Otherwise, two miners or validators (we’ll come back to this) could both validate the same transaction and waste time, energy, and money.
In order to gain money off of MATIC, you have to stake (own) a certain amount of MATIC. The more you own, the more likely you will be given the right to validate a transaction, and thus get the rewards of validating. With a little less minimum staking amount you could be a delegator, which is a person who picks validators for blocks.
Via SEBA Research
Looking to run an epic influencer marketing campaign on the newest platforms? NeoReach has the best experience in creating viral campaigns that convert on social media. Sign up here!
Validators vs Delegators
Let’s go over some of the terms you might have heard.
- Validators
these are people who make sure that the transactions happening on a blockchain are abiding by the rules and also make sure that the transaction hash (key) matches the transaction hash puzzle (lock). The hash is a 256-bit number that identifies data in a block. The lock is a mathematical problem and must result in the hash in order for it to be valid.
- Delegators
These people determine who is in charge of voting on Blockchain governance. These people do not play a part in the transactional process. They can propose alterations to the structure of the Blockchain. For instance, how big blocks should be, how many transactions can be validated in a block, and how much the validators should be paid.
These propositions are then brought to a vote so that users can vote. These people are voted in by stakes. The stakes can give their voting power to another entity to vote for them.
Via Medium
To stay updated on crypto news, check out this blog for the top crypto influencers.
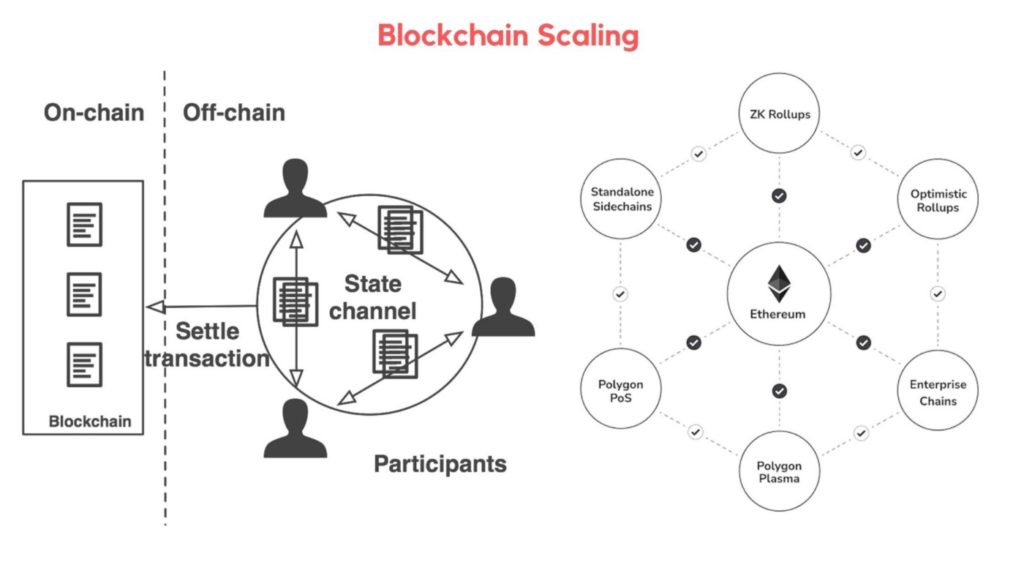
Plasma sidechains, ZK rollups, and Optimistic rollups
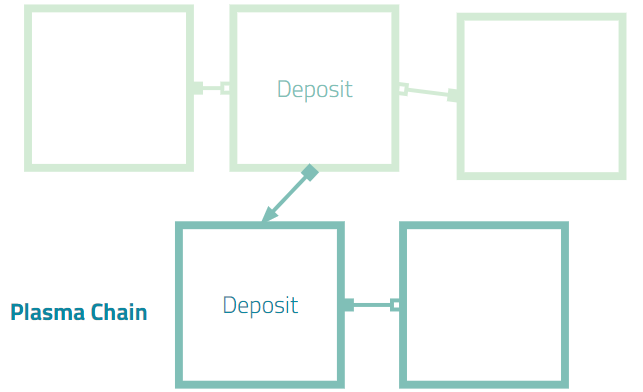
What is Polygon’s Plasma sidechain?
Polygon uses Plasma sidechains to communicate with the Ethereum blockchain and transfer assets safely into the Polygon blockchain. This is called a Blockchain bridge and allows Ethereum users to utilize Polygon technology, and vice versa.
Via Medium
By transferring files to Polygon, the Ethereum network doesn’t need to process as many files, making the blockchain quicker and more efficient
Via Medium
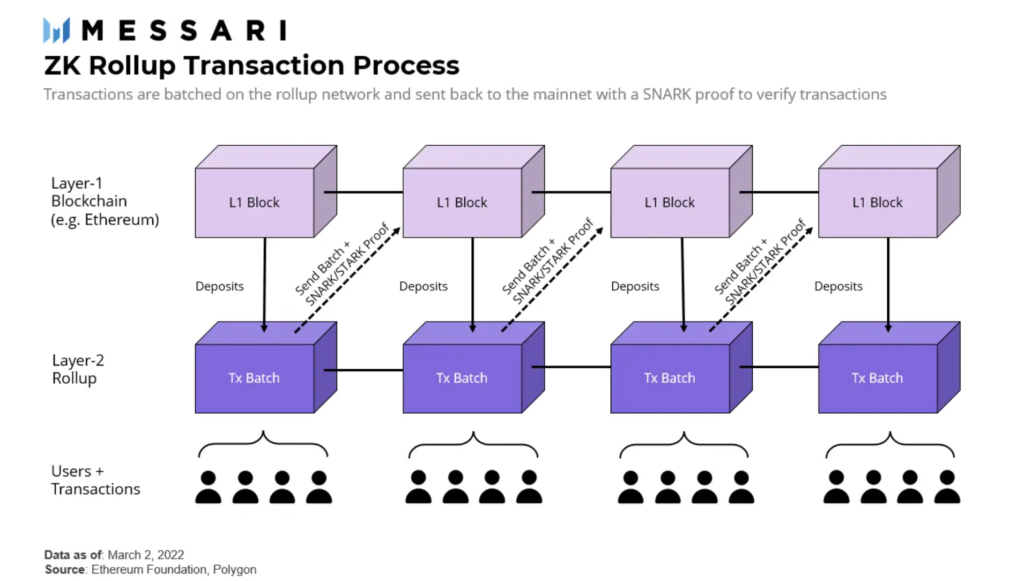
What is Polygon’s ZK rollup?
This implement is geared towards validating Ethereum transactions. It takes batches of Ethereum transactions, verifies them, then sends the bundle back to Ethereum with validity proofs. These are simplified versions of Ethereum blocks and make it so that Ethereum doesn’t have to store as much data on the chain.
Via Messari
What is Polygon’s Optimistic Rollup?
This is a security measure. If something is found to be faulty, the Polygon blockchain executes a fraud-proof protocol that determines the correct transaction. If someone submits a fraudulent transaction, the Polygon blockchain will slash the transaction.
How to Use Polygon
To use Polygon, a potential user only needs to buy them from an exchange. If you are new to cryptocurrency you can go with Coinbase and Binance. If you are more experienced you can go to a decentralized exchange like Uniswap. For Uniswap you need wrapped Ethereum (wETH).
Then, to transfer MATIC to a polygon wallet. You can find popular Polygon wallets on MetaMask ad Ledger. With this basic understanding of Polygon, you can dive into cryptocurrency investments.