Table of Contents
With the rapid popularity of crypto, processors barely had time to keep up with the sudden wide usage. This is where Avalanche comes into play, but what is Avalanche?
When Nakamoto created Bitcoin, he never could have imagined that this many people would use the system, network, and usage. The start of his project consisted of mining and creation of Bitcoin on Laptop processors.
But as time went on and Decentralized Financers and NFTs made use of blockchains, processing time became a real issue, leading to Blockchain Technology updates.
Ethereum became the next used currency for financing and NFT technology. However, the demand and usage of decentralized blockchains made Ethereum inadequate for the large number of transactions that were happening.
So financers and coders had to find a way to increase the number of transactions. One way they thought of doing so was to create a blockchain that had a faster transaction time, and lower gas fees for transactions.
What is Avalanche
Avalanche was developed to solve just this problem. It was led by Ava Labs and co-founded by Emin Gun Sirer, a computer science professor at Cornell University, and Moafan Yin, a coder who worked on Facebook’s now failed digital currency Libra.
Via Cornell Sun
Avalanche had a TPS (transactions per second) of 4,500. Compared to Ethereum’s 14 TPS, and Bitcoin’s TPS of 7.
Dr. Emin Gun Sirer wanted to make a cryptocurrency with the fastest time to finality, or how long it takes for a cryptocurrency to finish its transaction. To that end, Avalanche was a success. It achieves Time to Finality in 1 second, compared to Ethereum’s 1 minute.
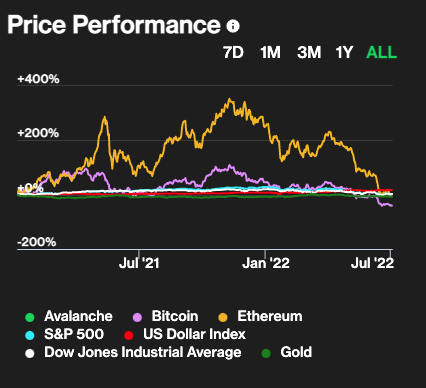
As of now, Avalanche has the 10th largest market cap with $33 billion. As of now, it is the largest blockchain with the most value locked in its protocol.
Via Coindesk
If you want to find out more about the best crypto partnerships, click here.
How does Avalanche work
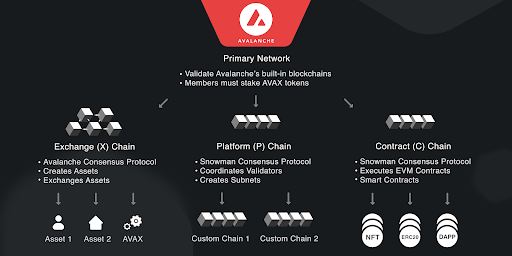
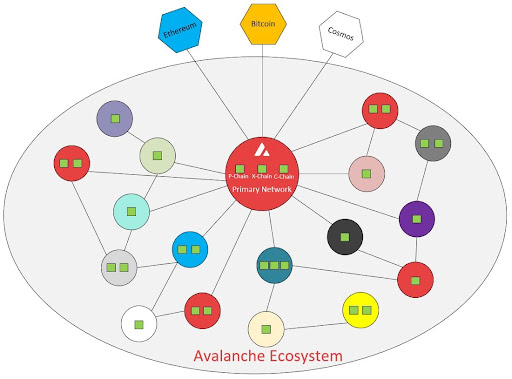
In easy terms, Avalanche utilizes 3 different blockchains to facilitate tasks, the reasoning being that each blockchain can easily do separate functions quicker than having one blockchain do all the tasks.
If you read about blockchain technology, they call the usage of a singular blockchain a layer 1 scaling solution. The usage of side-blockchains to validate is called a layer 2 solution, think about it as having 2 blockchains. Avalanche, while categorized as a layer 2 blockchain, utilizes 3 blockchains to facilitate its transactions.
More specifically, the Avalanche platform has to engage in Consensus protocols that work at reaching decisions amongst its participants. The Avalanche protocol is meant to combine the benefits of two types of Consensus protocols.
Via Medium
Classical protocols
These are the traditional ways of making decisions. They aren’t decentralized or scalable, but they are faster, greener, and cost less to maintain. Think about Meta Platform’s Libra project.
Nakamoto protocols
Named after Satoshi Nakamoto, Nakamoto protocols offer decision-making on a decentralized and scalable blockchain, working off of different computing nodes in its system. These are Scalable and Robust but lack the speed, efficiency, and cheapness of Classical protocols.
Looking to run an epic influencer marketing campaign using NFTs? NeoReach has the best experience in creating viral campaigns that convert on social media. Sign up here!
What is Avalanche’s Exchange Chain?
This chain is meant to create new assets, exchange between assets and facilitate cross-subnet transfers. This is for applications and isn’t for total ordering.
As of now, the Exchange chain’s most popular cryptocurrency is AVAX, but competitors like JOE and PNG are becoming more and more popular.
The transfers on the X-Chain are paid with AVAX. These payments are made as a way to facilitate network function.
What is Avalanche’s Contract Chain?
This Chain is the default smart contract blockchain and enables Ethereum-compatible smart contracts. This is because C-Chains are EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) compatible.
This feature is meant to allow developers to build decentralized applications while leveraging the platform’s security and scalability benefits.
This chain allows Ethereum apps, like DeFi Titan’s Aave to deploy a version of their product on Avalanche
What is Avalanche’s Platform Chain?
This chain is meant to keep track of metadata on a blockchain. Its purpose is the coordinate validators, keep track of active subnets, and allows for the creation of new subnets.
They also allow for the creation of L1 (Layer 1) or L2 (Layer 2) blockchains.
Via Avalanche
If you want to know more about DAO, crypto’s next big thing, click here.
Subnets
The importance of subnets cannot be understated. In a sense, subnets are blockchains that are created to support functionality.
Avalanche has 2 subnets that help facilitate. These subnets are clones of the default blockchain. For Avalanche, it is a clone of the Primary Network.
However, subnets can be created by users to help with network traffic when scaling limits are exhausted. Owing to this, Avalanche has quick transaction speeds – 2x faster than Visa.
In a theoretical sense, the ability to create new subnets creates an unlimited upper limit to the TPS limit. This means that transaction speeds could increase beyond 4,500 TPS.
Via Medium
Transaction Fees
Like Ethereum, Avalanche utilized transaction fees to pay for the network. Avalanche is based on the Ethereum EIP-1559 fee algorithm.
Ethereum’s gas fee is divided into being burned – and taken out of circulation to boost the value of other tokens – while the other half of the gas fee is paid to miners. On the other hand, Avalanche burns the entire gas fee.
This is CRAZY! #ethereum fees way too high, even ETH layer twos are "high" compared to #solana and #polygon $matic which have dirt cheap fees. pic.twitter.com/kv5MLDpMa8
— Lark Davis (@TheCryptoLark) January 13, 2022
To learn more about top crypto influencers to partner with in your next campaign click here.
How To Use Avalanche
In order to utilize the Avalanche blockchain, you have to get AVAX tokens which can be purchased on Binance and Kraken. You will then withdraw from this exchange and put it into the DeFi wallet (use the C chain, so as to not lose your AVAX tokens).
The C Chain runs on EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine). This means your Crypto wallet can have the same address for your Ethereum and your AVAX.